group
homepage
Russian version
Project smesher: generator of
single block and multiblock aggregated meshes around winged
bodies.
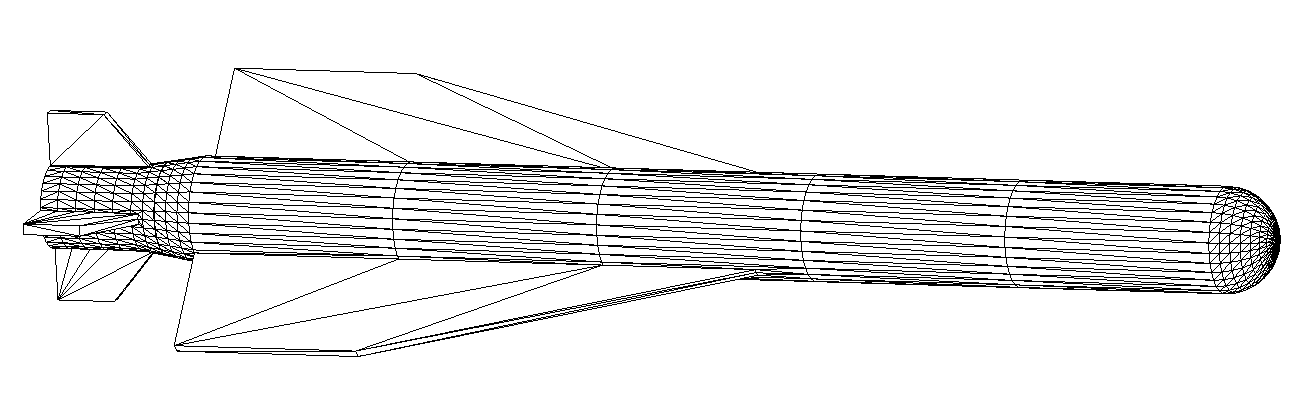
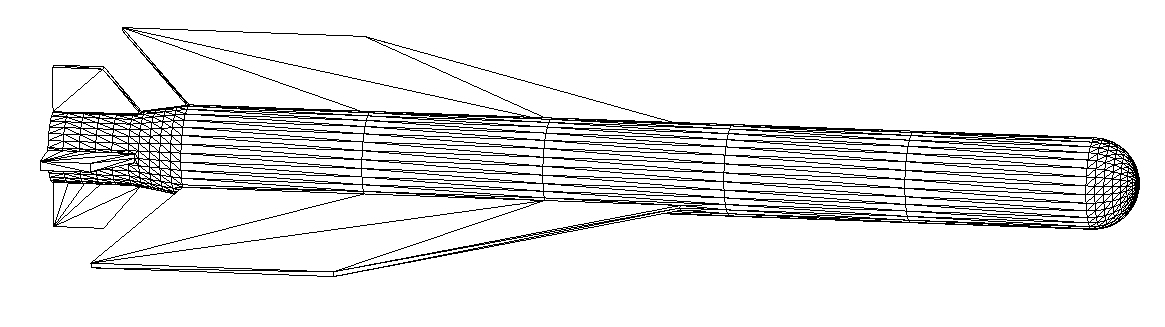
1) Model and initial tesselation.
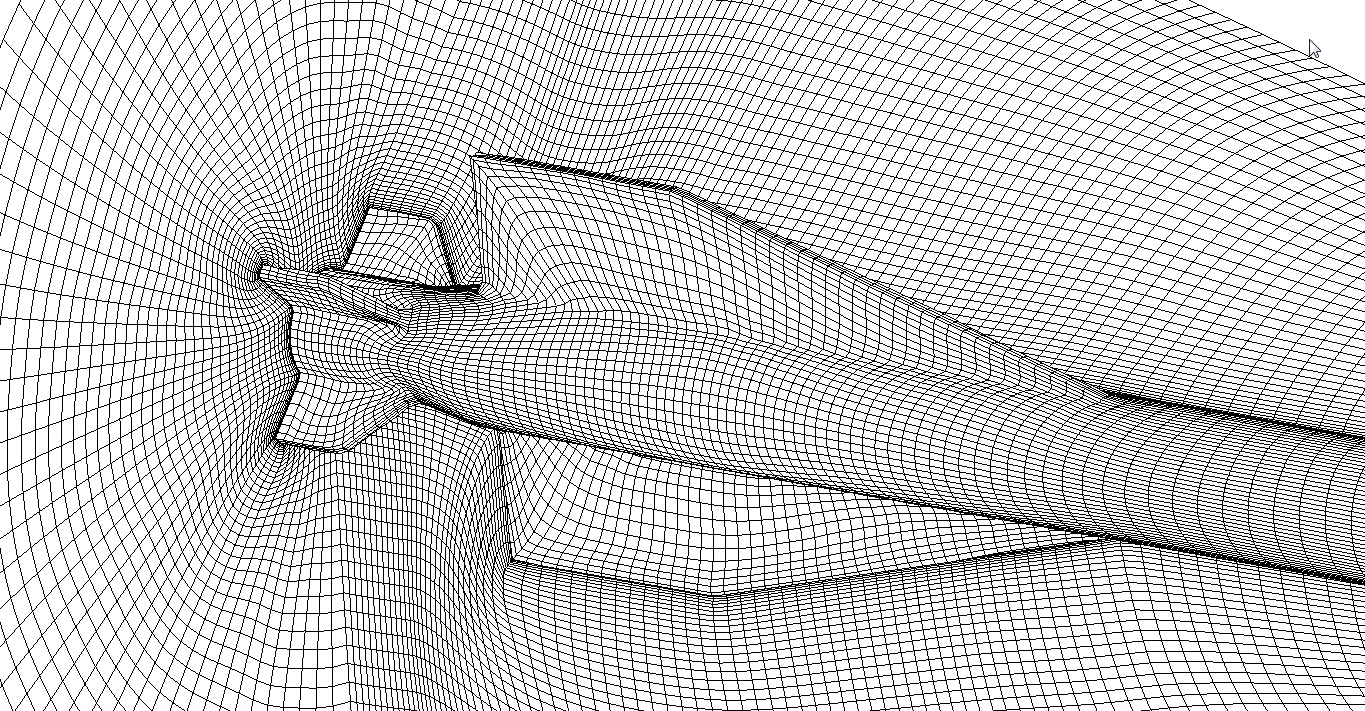
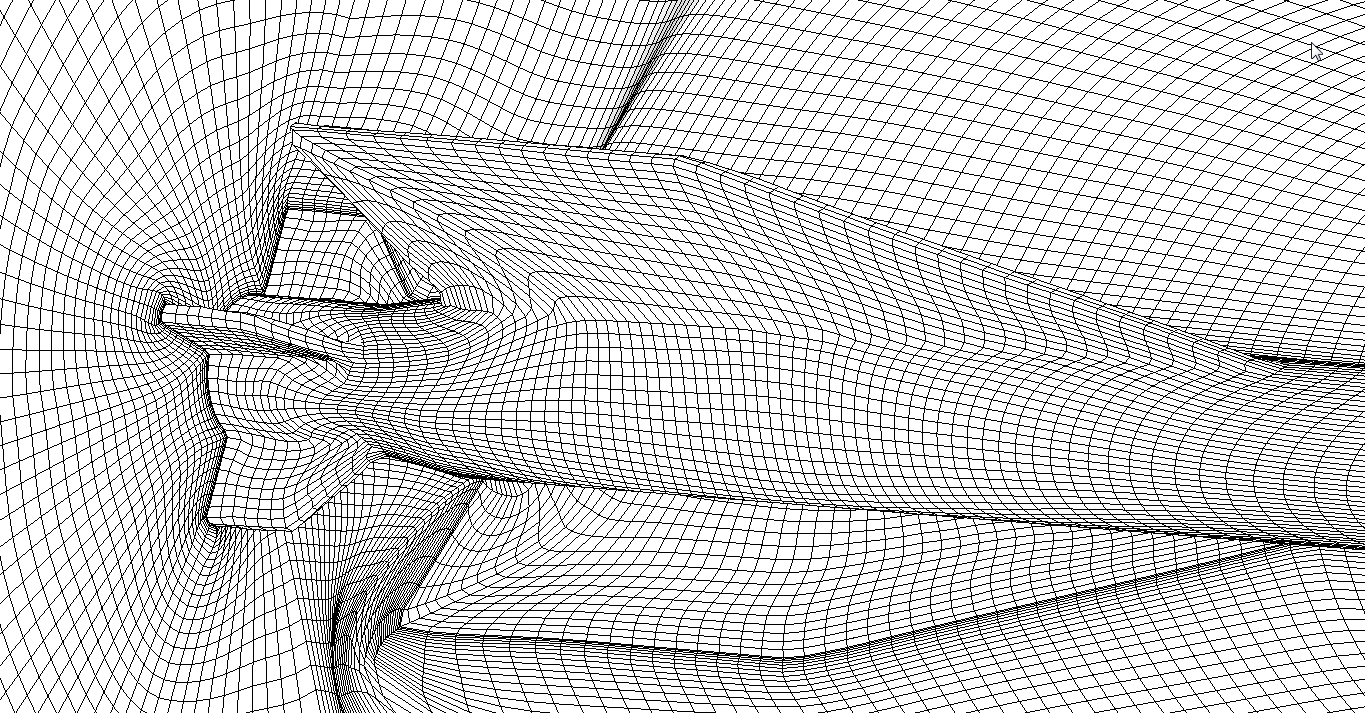
2) Fragment of tesselated surface and curvilinear surface mesh.
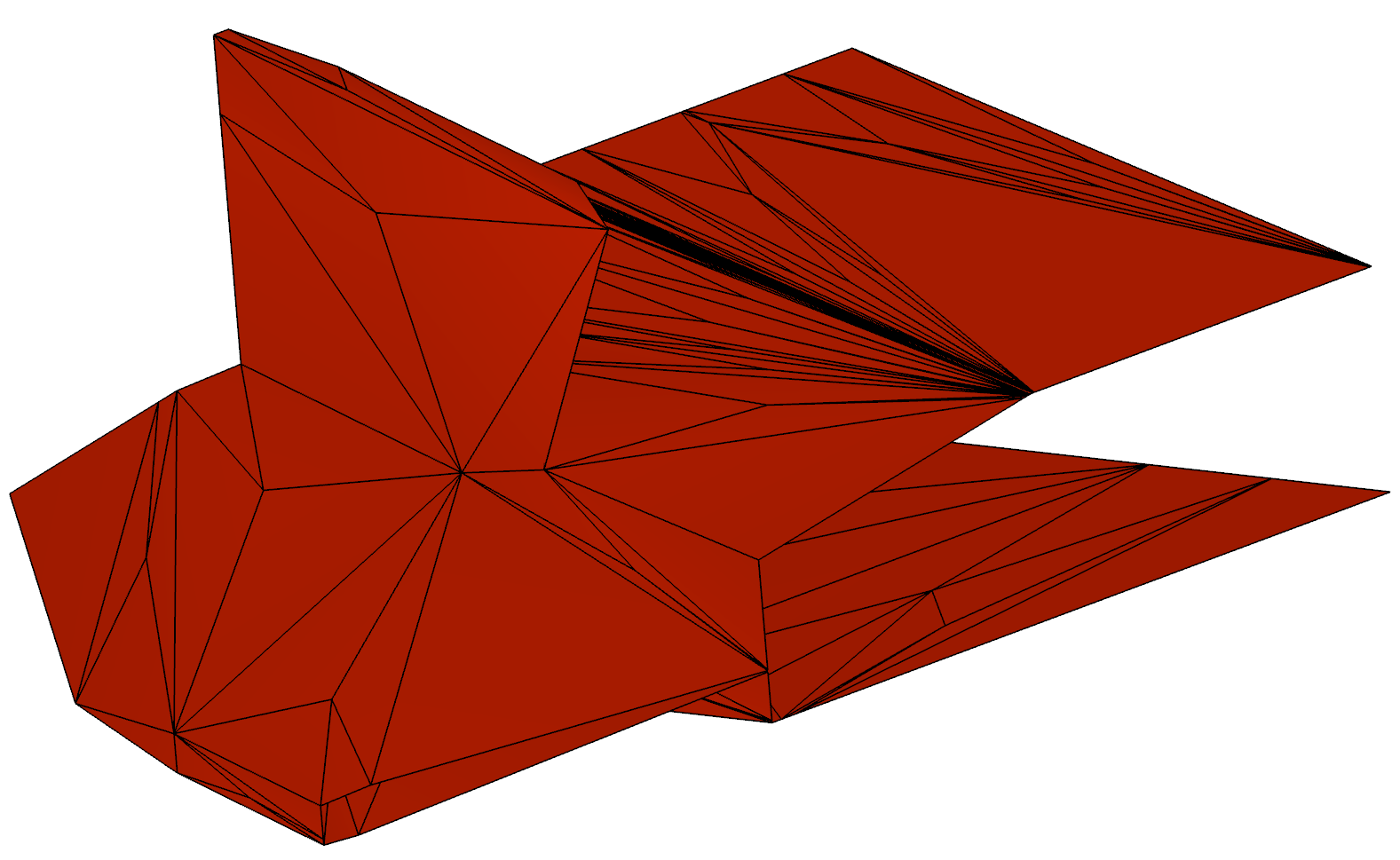
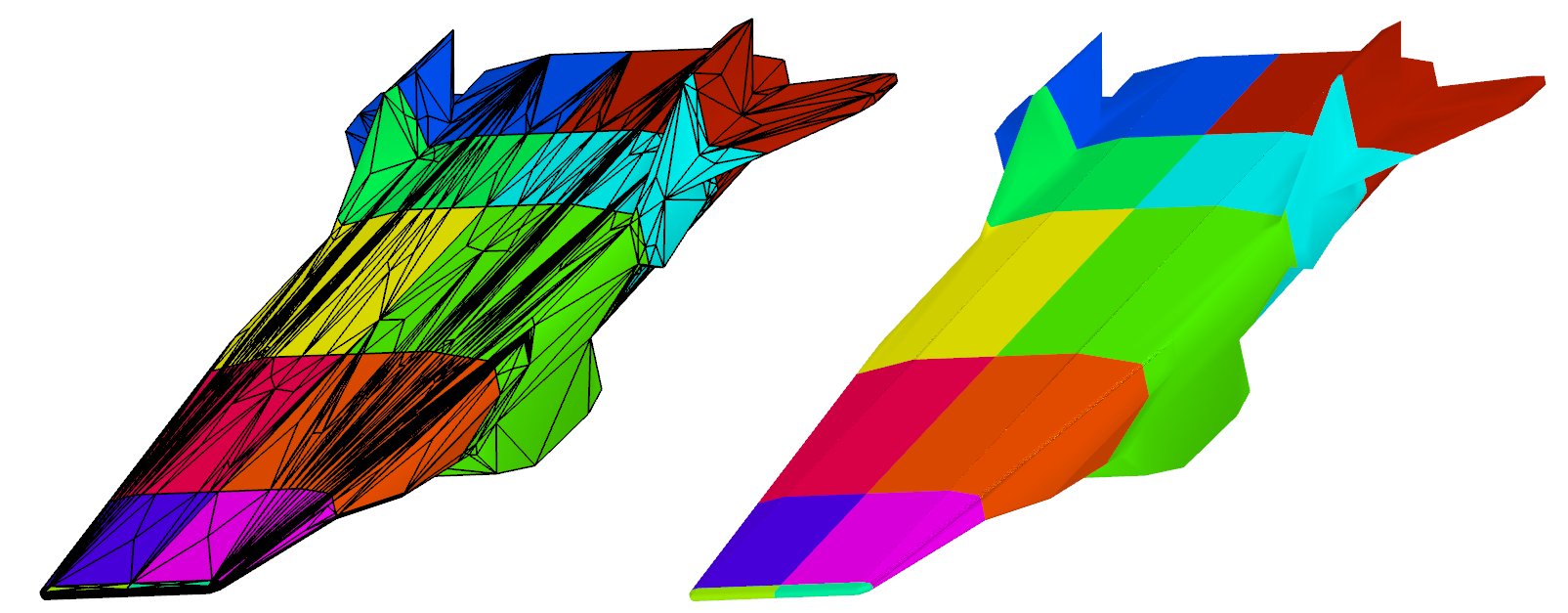
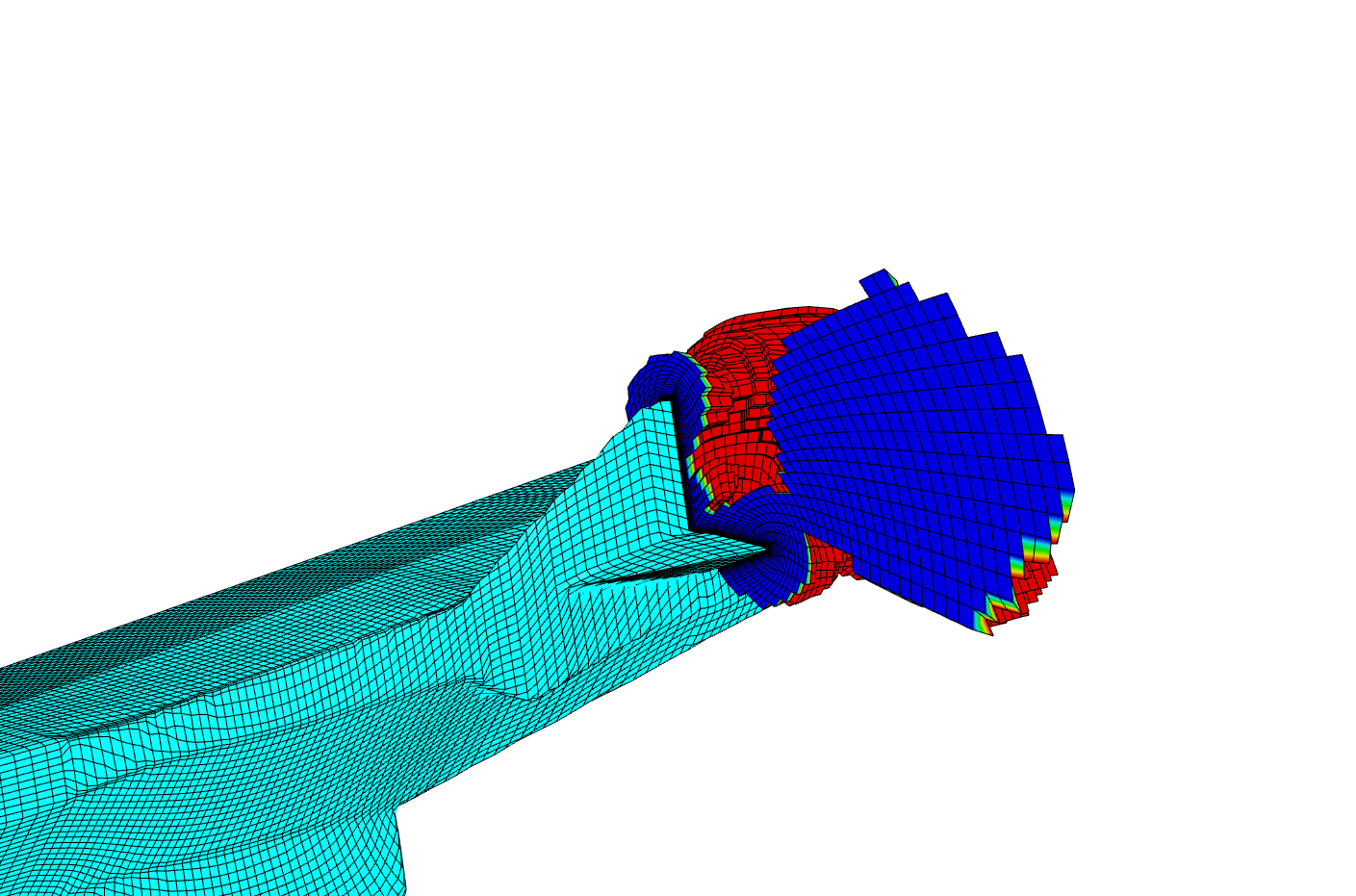
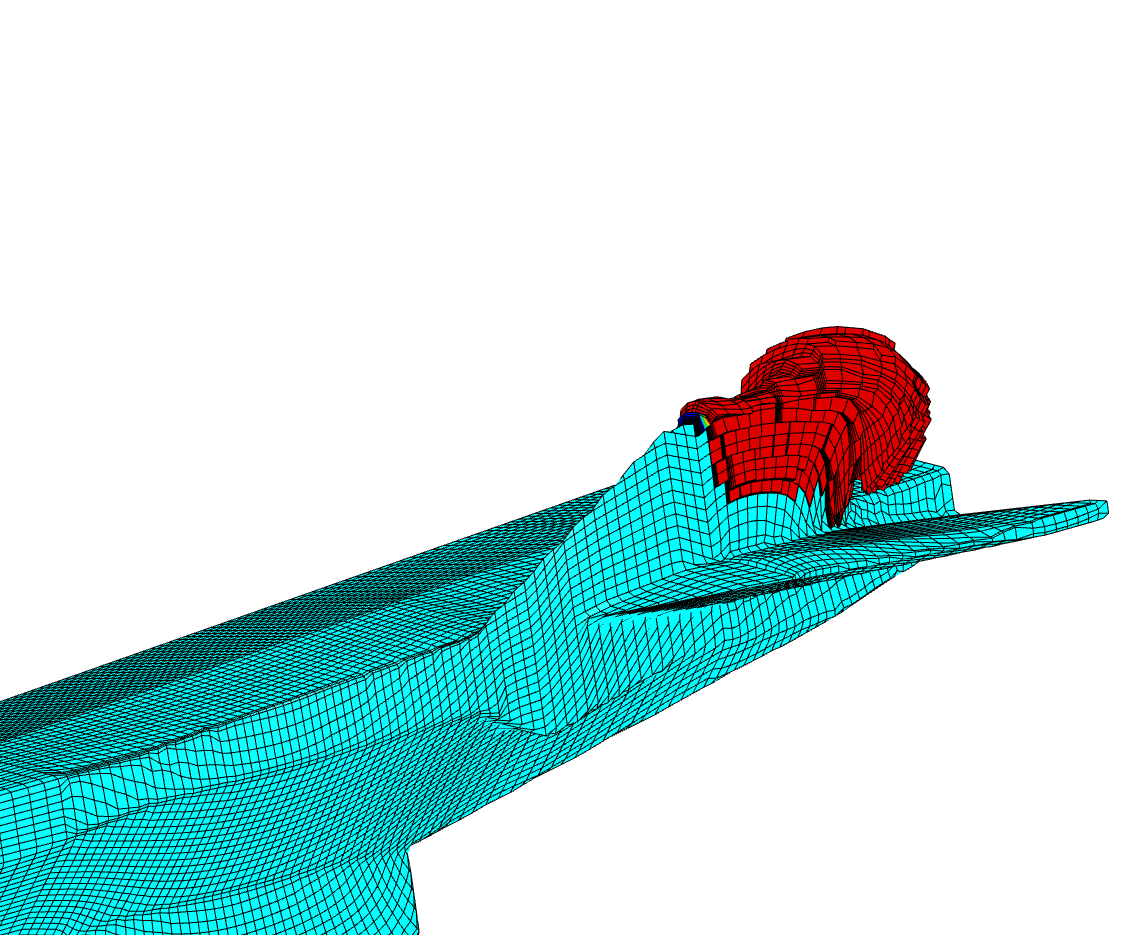
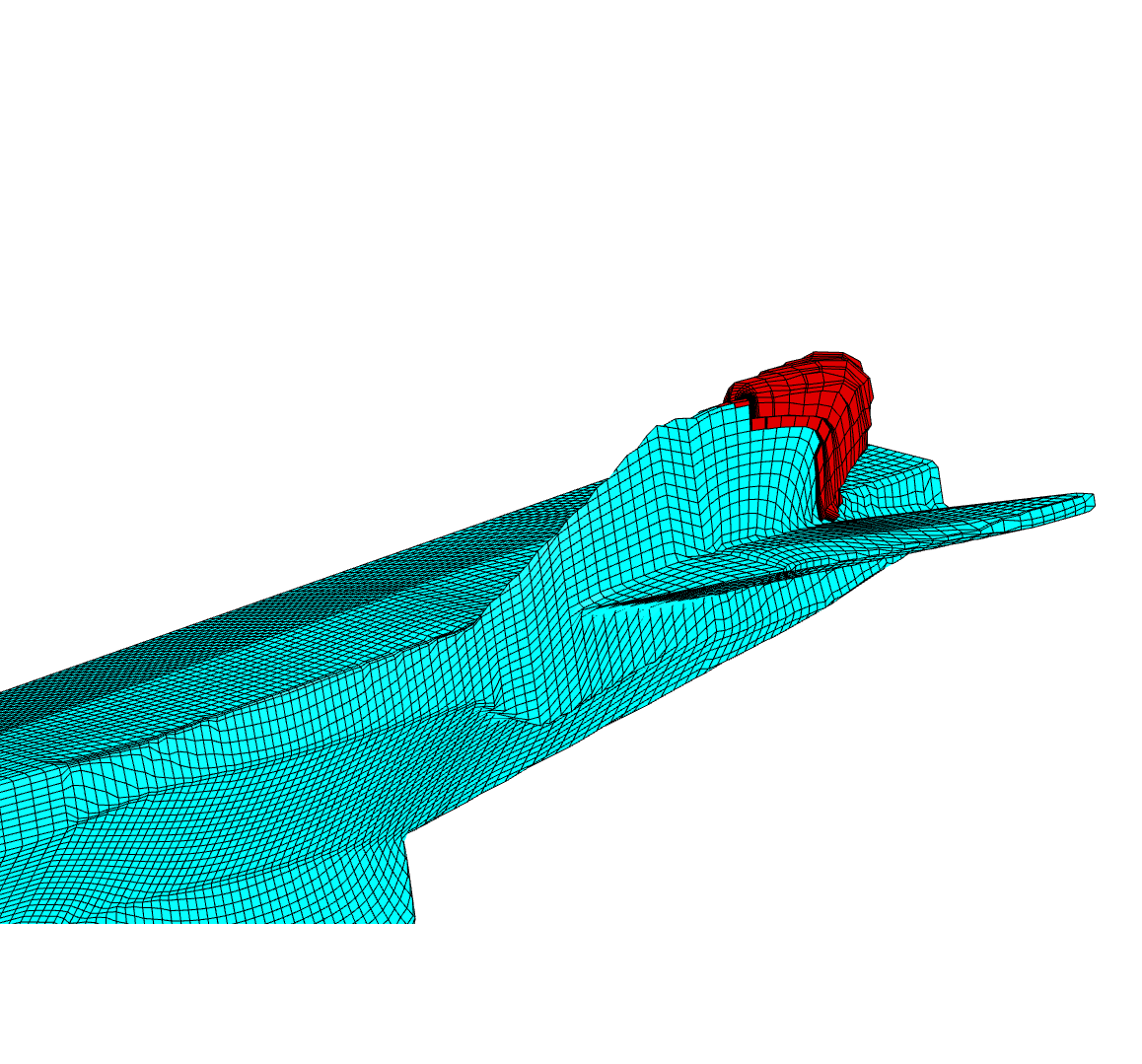
3) Adaptive untangling and optimization of 3d meshes. Algebraic
initial guess is constructed, active zone around bad cells is marked
and iterative untangling is applied locally. As soon as number of
bad cells is reduced by factor 100, active zone is recomputed. For
this test case active zone is recomputed four times in order to
untangle global mesh.
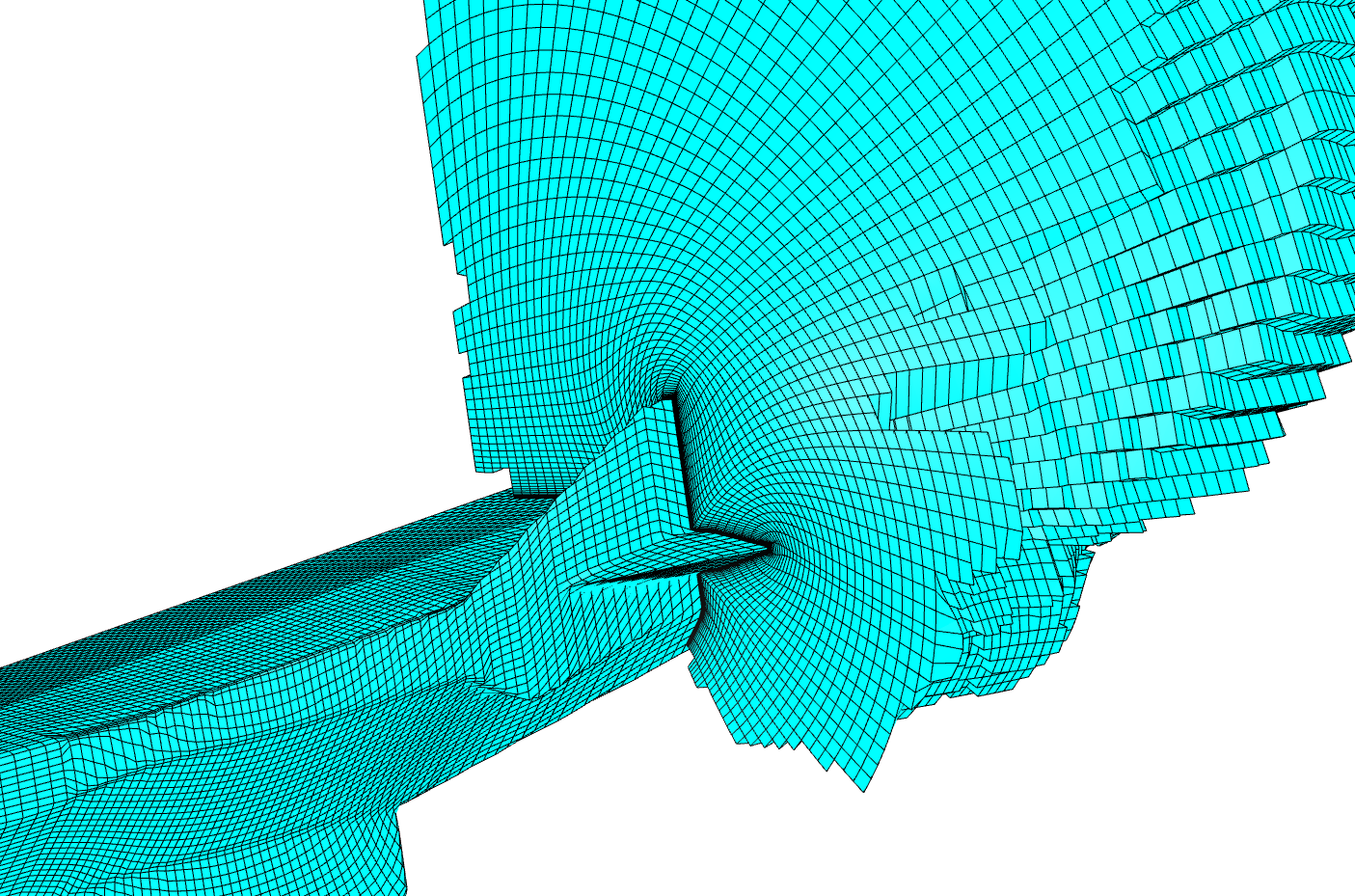
Example of adaptive surface mesh. Adaptation does not lead to cell
skewing for anisotropic cells.



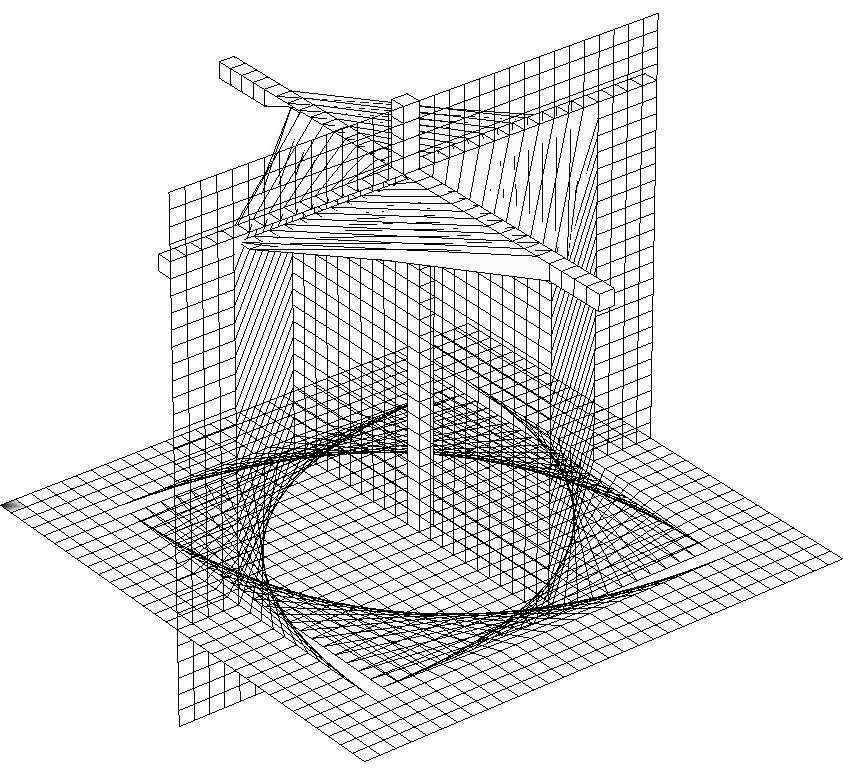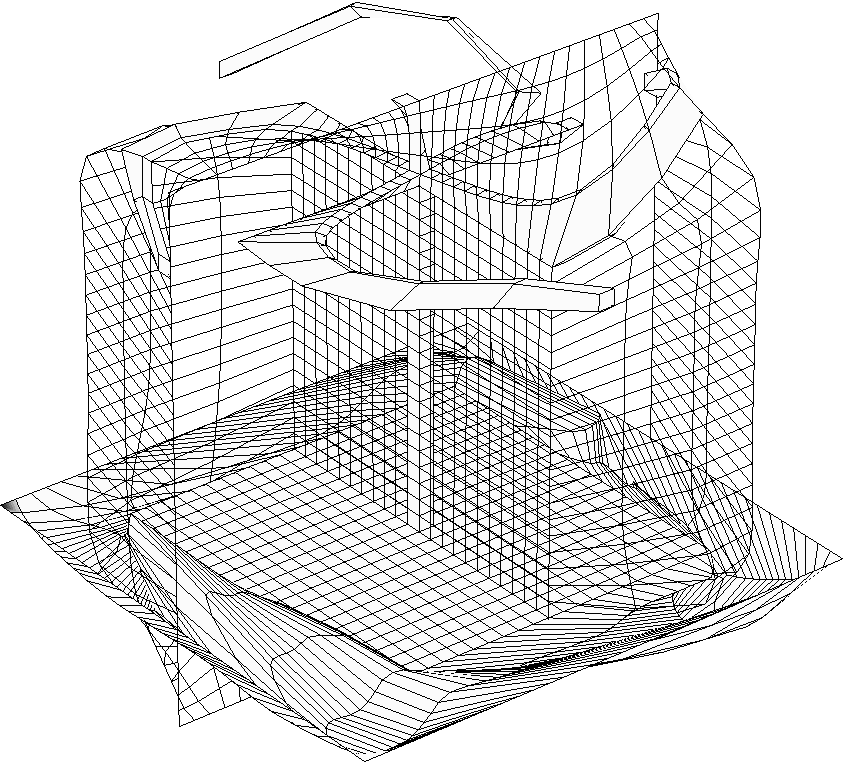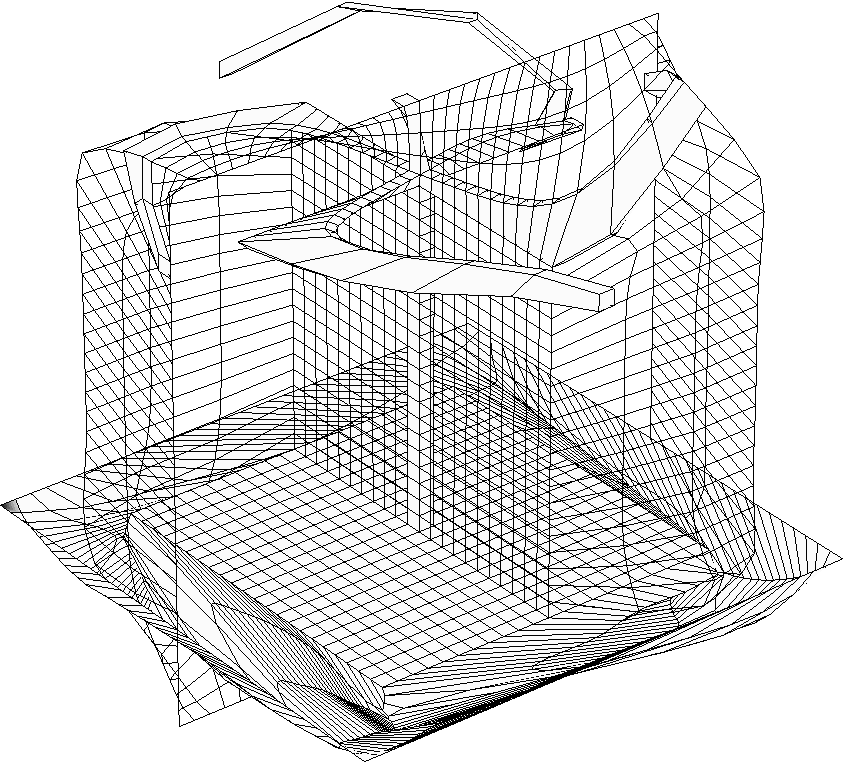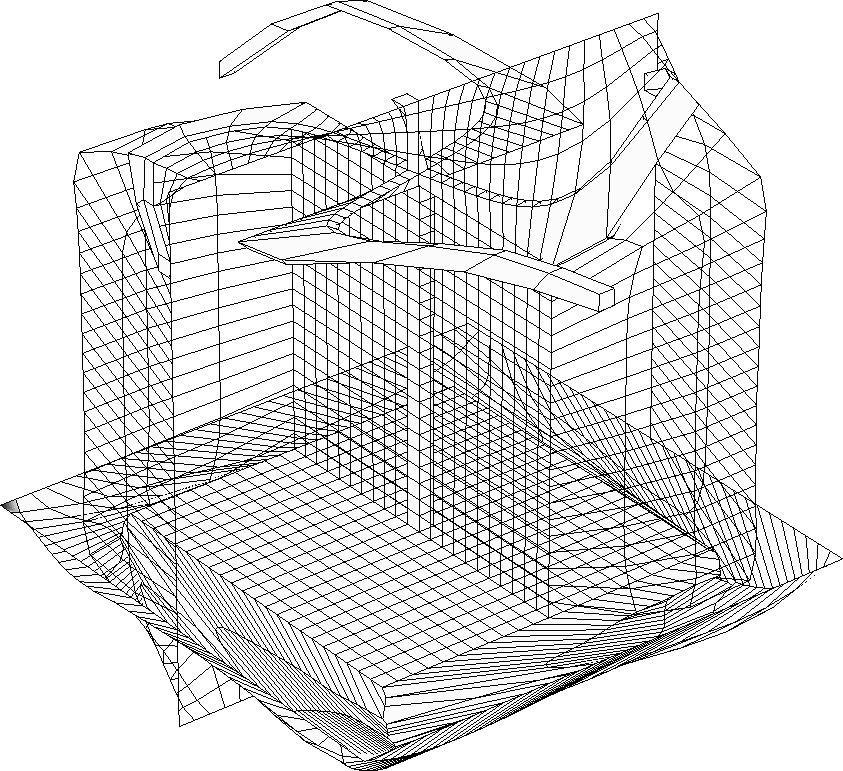
3d mesh around body and its refined version.
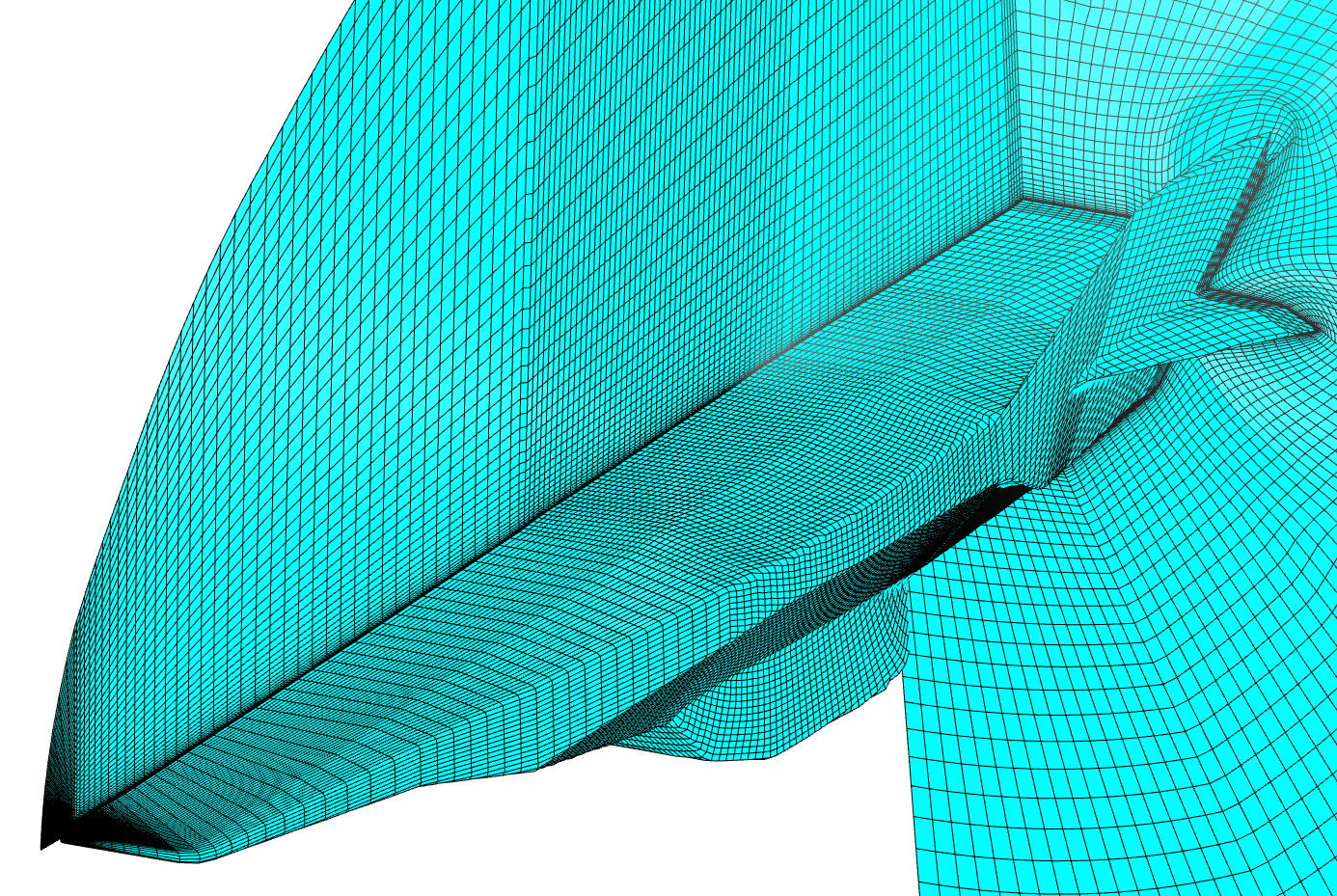

Meshing of simplified winged bodies. Initial teselation and final
uniform monoblock structured mesh is shown. Curvature adaptation is not
applied.
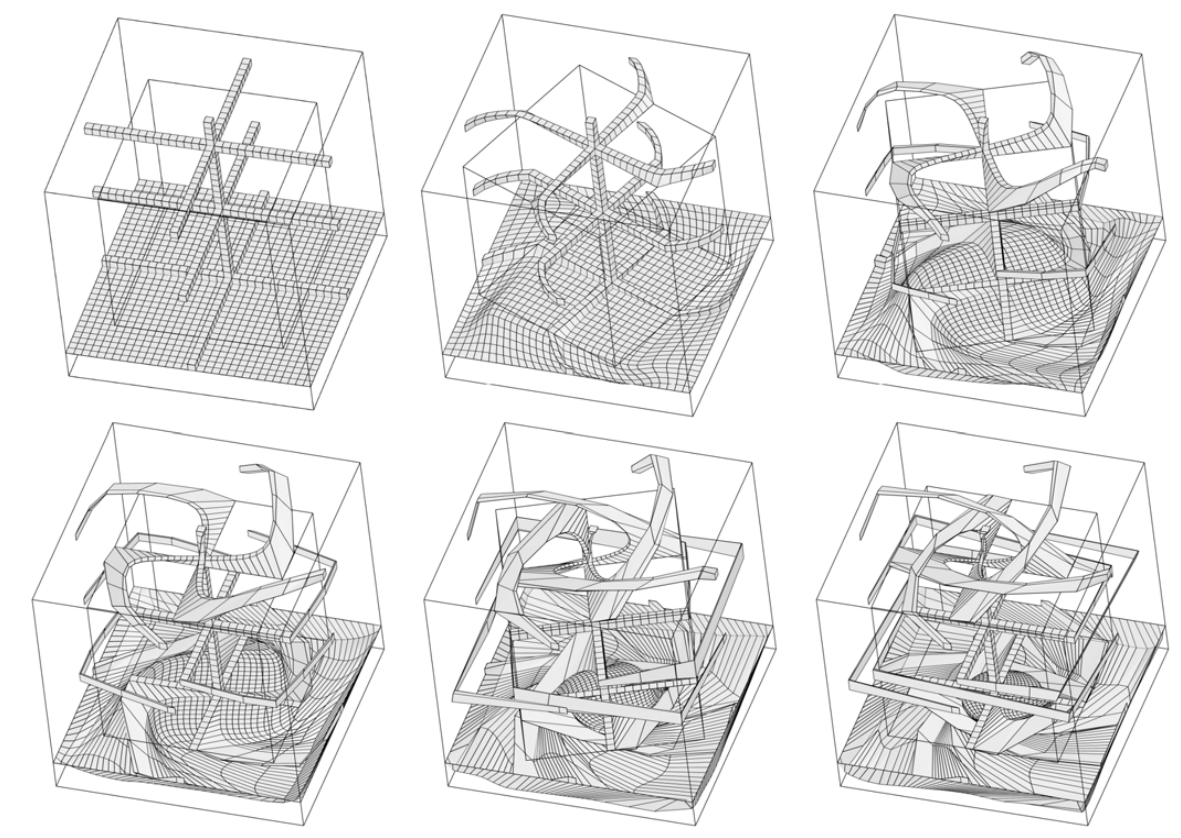
Example of mesh untangling in deformed geometry. Inner undeformed
cube is rotated inside larger cube around vertical axis.
Material between two cubes is hyperelastic one. Rotation
angles 0, pi/8, 3 pi / 8, pi/2, 7 \pi / 8, pi are considered.
Continuation procedure for nonsingular deformation here is
impossible since inner cube is intersects outer one when angle is
large enough. The untangling results are shown. The rows of deformed
hexahedral cells are images of rows made from the cubes under
deformation. In all test untangling was succesfull.
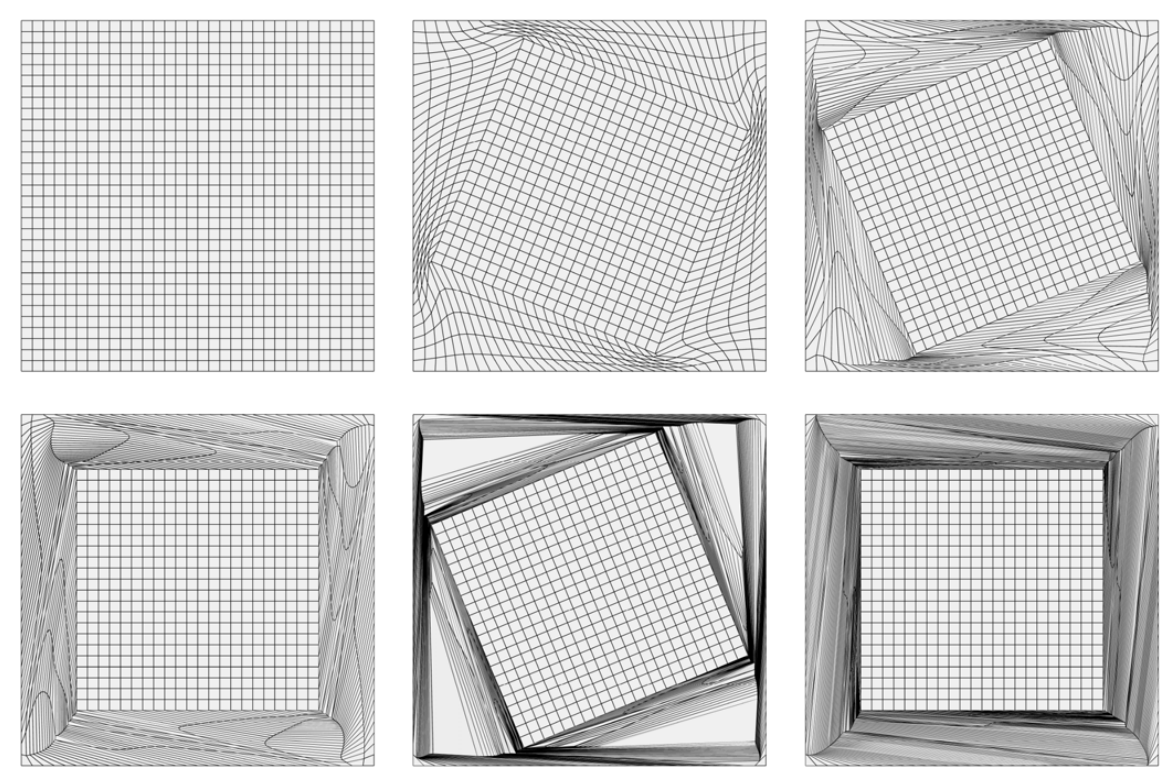
Behaviour of coordinate surface which is horizontal in original cube
and passes through central stiff cube.
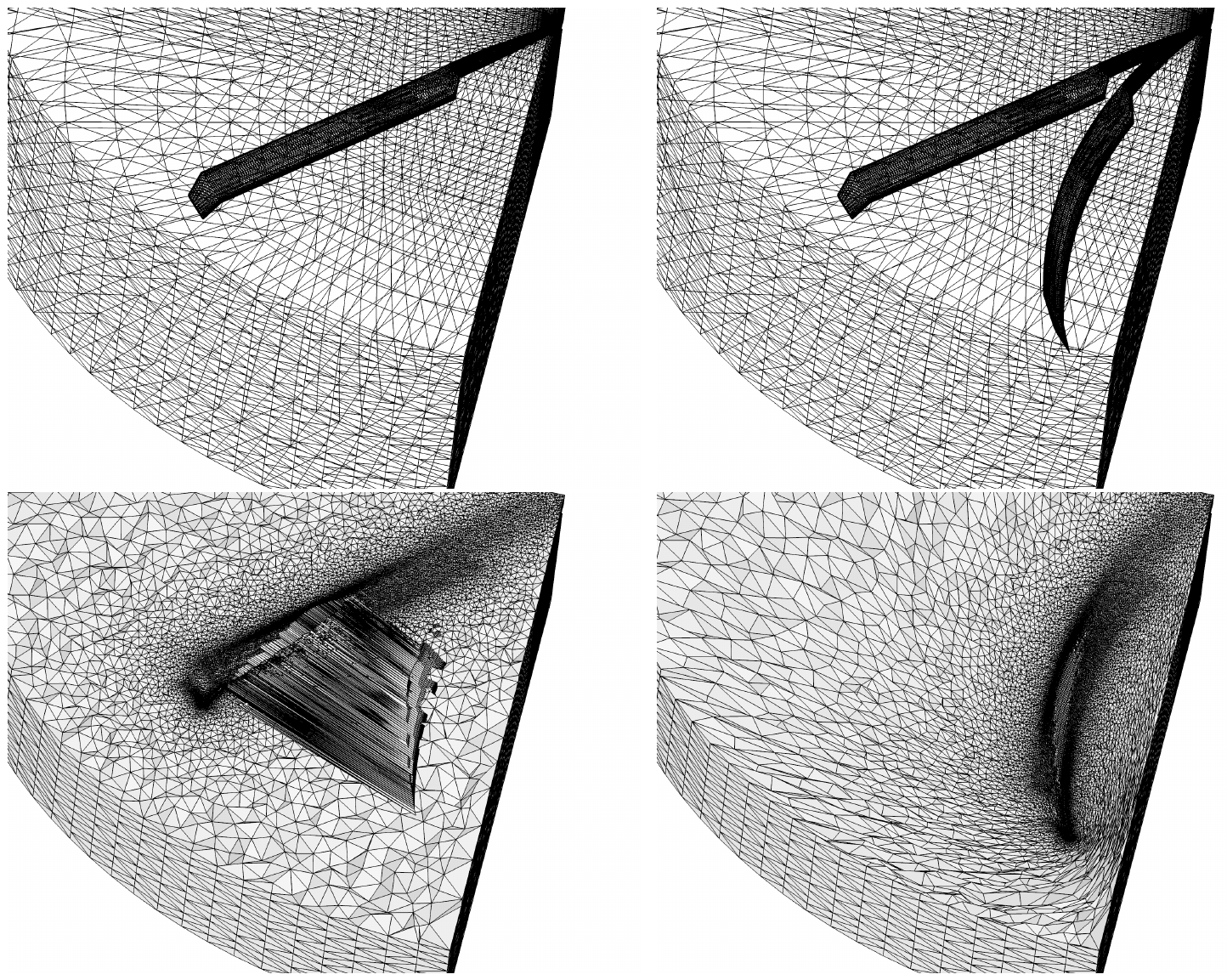
Example of tet mesh untangling after strong deformation of rotor
blades.
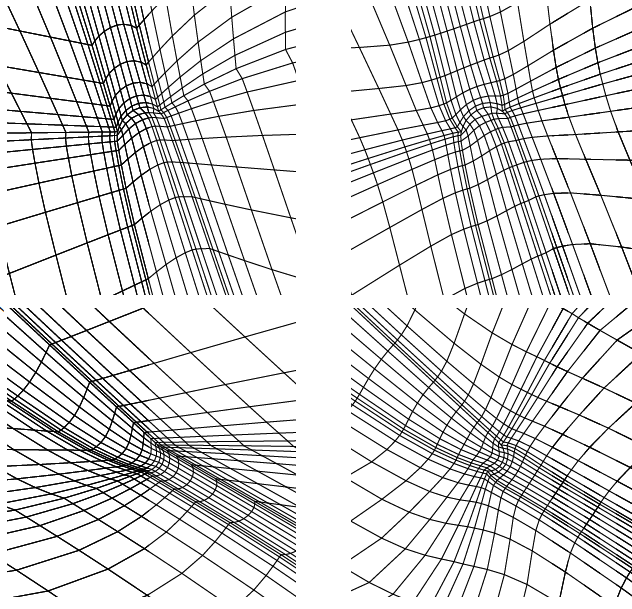
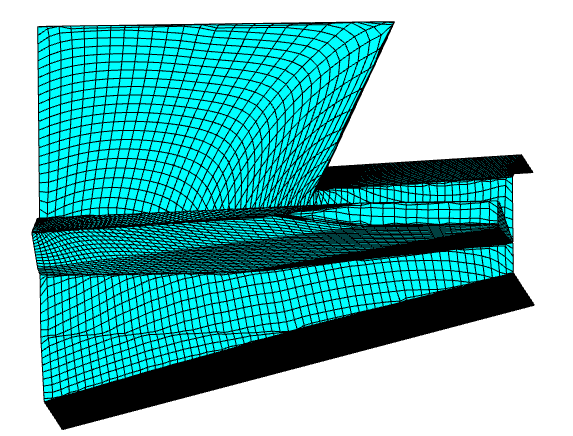
Mesh smoothing and orthogonalization in the key zones: near boundary
layers and subdomain boundaries. Example of coordinate surface of block
structured mesh of H-type. Left - block structured mesh
constructed using combination of algebraic and elliptic generator. Right
- variational smoothing and orthogonalization.